Heading:Sediments Study Tools and Techniques.
Introduction:What techniques do scientists use to study ocean Sediments?
Scientists also study sediments using seismic refraction.This is a technique that involves using an air gun and a hydrophone.
Every 1st sentence:As you would expect, modern oceanographers use tools far more sophisticated than those used a hundred years ago to study the ocean bottom.
Visuals and Vocabulary:
 This is a Clamshell Sampler and its an ocean sediment sampler with a set of jaws, designed to scoop up bottom sediment for research purposes; also called a grab sampler.
This is a Clamshell Sampler and its an ocean sediment sampler with a set of jaws, designed to scoop up bottom sediment for research purposes; also called a grab sampler. This is a Grab Sampler and its an ocean sediment sampler with a set of jaws, designed to scoop up bottom sediment for research purposes; also called a Clamshell Sampler.
This is a Grab Sampler and its an ocean sediment sampler with a set of jaws, designed to scoop up bottom sediment for research purposes; also called a Clamshell Sampler.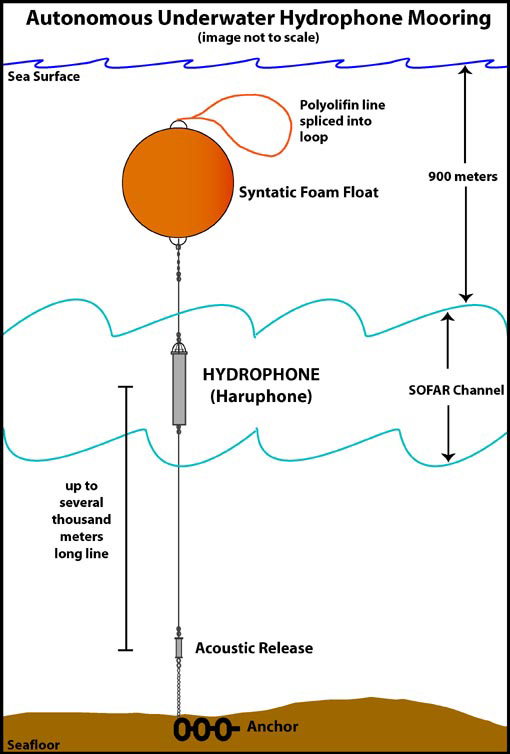 This is a Hydrophone and its an underwater microphone.
This is a Hydrophone and its an underwater microphone. This is a Seismic Refraction and its a technique used to study marine sediments; equipment includes an airgun aboard avessel to produce the reflected sound and a towed hydrophone to detect the reflected sound waves.
This is a Seismic Refraction and its a technique used to study marine sediments; equipment includes an airgun aboard avessel to produce the reflected sound and a towed hydrophone to detect the reflected sound waves.End of reading:N/A
Summary:N/A
Title:The Study of Sediments.
Heading:Stratigraphy and Paleoceanography.
Introduction:How do scientists use ocean sediments to study the past?
Scientists use deep-sea stratigraphy to look for clues, such as rock composition, microfossils, deposition patterns, and other physical properties.
Every 1st sentence:AS you will learn in more detail shortly, sedimentation is an on going process.
Visuals and Vocabulary:
 This is a Stratigraphy and its the study of Sediment layers.
This is a Stratigraphy and its the study of Sediment layers.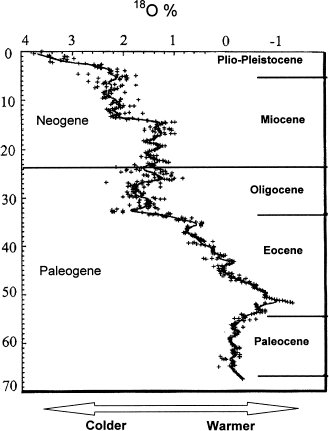 This is Paleoceanography and its the study of prehistoric ocean.
This is Paleoceanography and its the study of prehistoric ocean.End of reading:
Summary:



